产品描述
*The optimal dilutions should be determined by the end user. For optimal experimental results, antibody reuse is not recommended.
*Tips:
WB: 适用于变性蛋白样本的免疫印迹检测. IHC: 适用于组织样本的石蜡(IHC-p)或冰冻(IHC-f)切片样本的免疫组化/荧光检测. IF/ICC: 适用于细胞样本的荧光检测. ELISA(peptide): 适用于抗原肽的ELISA检测.
引用格式: Affinity Biosciences Cat# AF5354, RRID:AB_2837839.
展开/折叠
Activator protein 1; AP 1; C FOS; Cellular oncogene c fos; Cellular oncogene fos; FBJ murine osteosarcoma viral (v fos) oncogene homolog (oncogene FOS); FBJ murine osteosarcoma viral oncogene homolog; FBJ murine osteosarcoma viral v fos oncogene homolog; FBJ Osteosarcoma Virus; FOS; FOS protein; FOS_HUMAN; G0 G1 switch regulatory protein 7; G0/G1 switch regulatory protein 7; G0S7; Oncogene FOS; p55; proto oncogene c Fos; Proto oncogene protein c fos; Proto-oncogene c-Fos; v fos FBJ murine osteosarcoma viral oncogene homolog;
抗原和靶标
A synthesized peptide derived from human c-Fos, corresponding to a region within N-terminal amino acids.
研究领域
· Cellular Processes > Cell growth and death > Apoptosis. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > MAPK signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > cAMP signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Environmental Information Processing > Signal transduction > TNF signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Drug resistance: Antineoplastic > Endocrine resistance.
· Human Diseases > Substance dependence > Amphetamine addiction.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Bacterial > Salmonella infection.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Bacterial > Pertussis.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Parasitic > Leishmaniasis.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Parasitic > Chagas disease (American trypanosomiasis).
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Viral > Hepatitis B.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Viral > HTLV-I infection.
· Human Diseases > Infectious diseases: Viral > Herpes simplex infection.
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Overview > Pathways in cancer. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Colorectal cancer. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Specific types > Breast cancer. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Cancers: Overview > Choline metabolism in cancer. (View pathway)
· Human Diseases > Immune diseases > Rheumatoid arthritis.
· Organismal Systems > Development > Osteoclast differentiation. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Immune system > Toll-like receptor signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Immune system > IL-17 signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Immune system > Th1 and Th2 cell differentiation. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Immune system > Th17 cell differentiation. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Immune system > T cell receptor signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Immune system > B cell receptor signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Environmental adaptation > Circadian entrainment.
· Organismal Systems > Nervous system > Cholinergic synapse.
· Organismal Systems > Nervous system > Dopaminergic synapse.
· Organismal Systems > Endocrine system > Estrogen signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Endocrine system > Prolactin signaling pathway. (View pathway)
· Organismal Systems > Endocrine system > Oxytocin signaling pathway.
· Organismal Systems > Endocrine system > Relaxin signaling pathway.
文献引用
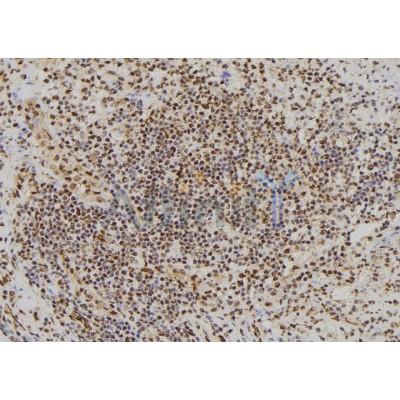
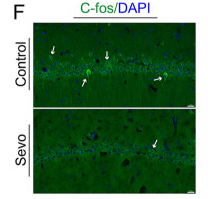
Application: IF/ICC Species: Rat Sample: hippocampal
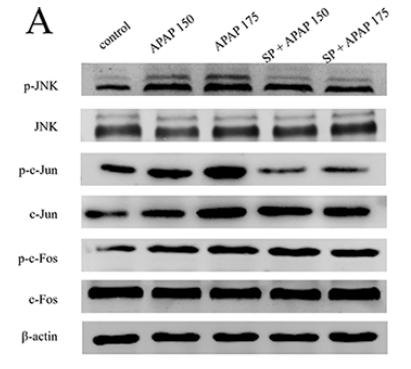
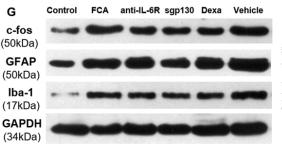
Application: WB Species: Rat Sample:
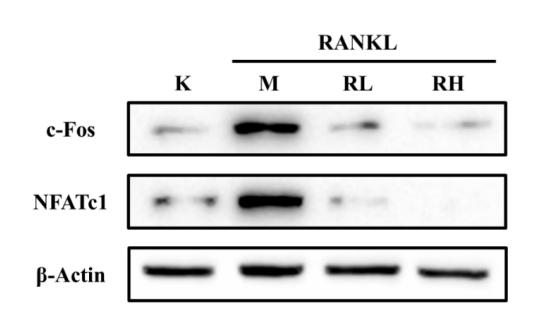
Application: WB Species: Sample: RAW264.7 cells
Application: WB Species: Mouse Sample:
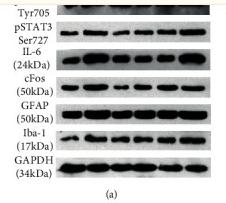
Application: WB Species: mouse Sample: liver
限制条款
产品的规格、报价、验证数据请以官网为准,官网链接:www.affbiotech.com | www.affbiotech.cn(简体中文)| www.affbiotech.jp(日本語)产品的数据信息为Affinity所有,未经授权不得收集Affinity官网数据或资料用于商业用途,对抄袭产品数据的行为我们将保留诉诸法律的权利。
产品相关数据会因产品批次、产品检测情况随时调整,如您已订购该产品,请以订购时随货说明书为准,否则请以官网内容为准,官网内容有改动时恕不另行通知。
Affinity保证所销售产品均经过严格质量检测。如您购买的商品在规定时间内出现问题需要售后时,请您在Affinity官方渠道提交售后申请。产品仅供科学研究使用。不用于诊断和治疗。
产品未经授权不得转售。
Affinity Biosciences将不会对在使用我们的产品时可能发生的专利侵权或其他侵权行为负责。Affinity Biosciences, Affinity Biosciences标志和所有其他商标所有权归Affinity Biosciences LTD.